Wayfair is a company that believes growth is built on a strong global presence. Localization is a key element in successfully establishing ourselves in many markets and achieving the desired growth.
Our Localization Engineering teams are committed to: providing the best customer experience, optimizing cost and efficiency, and driving innovation. We have developed an array of advanced solutions that are integrated with software services to automate translation processes executing millions of translation requests daily. In this article, we will cover one of these solutions.
Translation Workflows
Vetting the data for products being added to our catalog is a resource-intensive process, especially when those products are to be sold in multiple languages. Our aim was to facilitate rapid catalog growth while minimizing costs for product addition and content localization, all while maintaining high translation quality. To achieve this objective, we introduced configurable translation workflows to our Localization System.
Each translation workflow is a set of rules that determine translation methods, their order, behaviors, and impact on translation eligibility that governs which content can and cannot be displayed to customers.
Let’s take a look at an example of a product content translation that is applicable across most e-commerce businesses. A product description usually contains primary information such as a product title, an option name, and some form of free text describing the product (e.g., a romance copy) that needs to be translated.
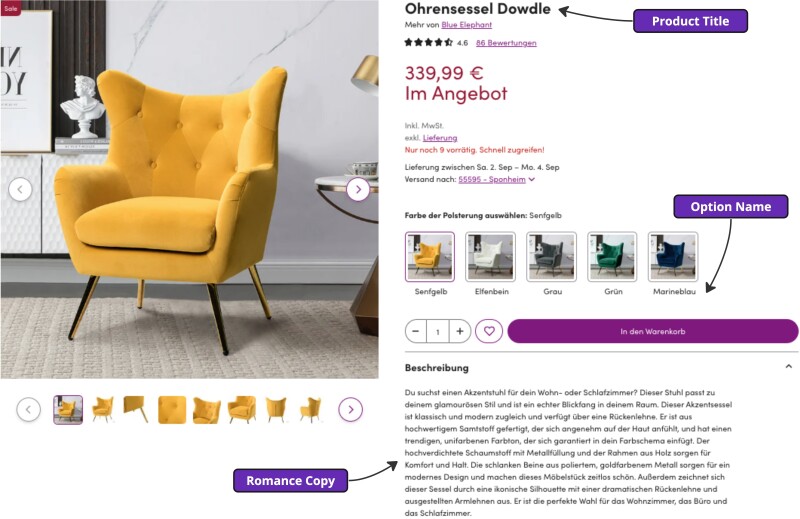
Each content type such as a title or an option name has its own translation complexity and quality expectations that vary based on text length, context, and other factors. A complicating factor is that there are many variables and exceptions that can affect the desired quality and affordable cost of translation. For instance, top sellers might always demonstrate a high return on investment that requires the best translation quality for all content, necessitating human translation.
This variability means that a machine translation method will work well for some content, but not all. However, it must be used whenever it can meet quality requirements to achieve efficiency, because pure human translation would be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming.

The Translation Workflows engine allows us to configure translation methods (e.g., machine, human and its different vendors and flavors) at a very granular level. Configurations can be set globally from a source locale to a target locale, for a category, a specific product, a product title, option category, reaching infinite levels or combinations of content types being extensible for other use-cases. This system enables us to tune and maintain translation processes considering desired translation cost, quality, and time.
Configuration Formula:
[Source Locale] [Target Locale] [Content Type] [...] [N] => [Translation Method]
When a formula is applied, the most precise configuration gets the highest priority. Meaning, if there is a configuration to translate a particular product A by a human translator, it will be chosen over a default configuration that is only specified using a source locale to a target locale value.
Configuration examples:
- [en_UK] [de_DE] [all content] => [Human Translation]
- [en_UK] [de_DE] [option name] => [Machine translation]
- [en_UK] [de_DE] [option name] [category beds] => [Human Translation]
- [en_UK] [de_DE] [product A] [upholstery option names] => [Machine Translation]
- [en_UK] [de_DE] [romance copy] => [No Translation]

Currently, we have a variety of such configurations that are created based on analysis and business requirements. In most cases, configurations are created and upgraded automatically (e.g., top sellers translated by human translators), with the minimal manual effort needed to maintain and tune.
On the following chart you can see a simplified version of catalog translation processes. Where the Translations Workflow Configuration engine determines a translation method based on a predefined configuration.

Advanced Translators
In order to benefit from the Translation Workflows at full scale, we introduced a concept of Advanced Translators. Every translation should be done as quickly as possible to ensure a great customer experience. However, human translations can delay content localization, blocking a product from being on site for a few days. To mitigate this, we introduced Advanced Translators that aggregate multiple synchronous translation steps, rolling forward the translation progress gradually.
Let’s zoom into two Advanced Translators which are used to ensure that translations happen quickly and guarantee high quality eventually:
Combined: a set of translators (i.e., machine, word replacement, human) that run one after another, where each subsequent translator overrides any existing translation, upgrading quality.
- This way machine translation will make the new language available immediately, while a human translation will be requested simultaneously. Once the human translation is done, the previous machine translation will be replaced by the new text, upgrading quality. This also enables machine translation to be utilized during human translation (e.g., post-editing), accelerating the process.
Optional: similar to combined, but an existing translation will be overwritten only by the last translator. In other words, machine translation is skipped if a prior translation already exists.
- The existing translation might be not relevant (e.g. source data drastically changed) but the overall quality of it will remain high and accurate. For instance, if marketing content is modified, we do not want to drop the quality to machine level and prefer to wait for human translation to change the translated text.
Formula: [Combined/Optional] [Translator 1] => [Translator 2] => [Translator N]
Examples:
- [Combined] [*Machine Translation Vendor 1] => [Human Translation]
- [Combined] [Machine Translation Vendor 2] => [Human Translation]
- [Optional] [Machine Translation] => [Human Translation]
- [Optional] [Machine Translation] => [Word Replacement] => [Human Translation]
* Multiple different vendors or variants are used due to aspects of translation quality or machine learning training sets that perform better for different languages.
The Advanced Translators are used as a translation method in the Workflows. In such a case, we guarantee that users get translations in near-real-time with a promise to provide better quality later (e.g., after human translation completion).

Conclusion
In recent years, we launched a range of services that harmonize translation workflows, effectively managing the trade-off between speed and costs. Our adaptable and scalable solutions empower us to expand our international product offerings significantly, easily replace translation vendors to gain efficiency, and tune localization processes based on market needs.
We continue to invest in Localization space with relentless customer focus supporting rapid and extensive global growth of Wayfair.
